By: Team W10-3 Since: Aug 2018 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. How it works, in brief
- 4. Special Considerations
- 5. Features
- 5.1. View help :
help - 5.2. User Commands
- 5.2.1. Add a user :
addUser - 5.2.2. Login a user :
login - 5.2.3. Logout a user :
logout - 5.2.4. List all users :
listUser - 5.2.5. Find users by name, phone number, email, address, interest, tag :
findUser - 5.2.6. Delete a user :
deleteUser - 5.2.7. Select a user :
selectUser - 5.2.8. Edit a user :
editUser - 5.2.9. Add a friend :
addFriend - 5.2.10. Delete a friend :
deleteFriend - 5.2.11. Suggest friends based on similar interests :
suggestFriendsByInterests - 5.2.12. List all friends of a user :
listFriends - 5.2.13. Get free time between users :
maxSchedule
- 5.2.1. Add a user :
- 5.3. Create and confirm event commands
- 5.3.1. Create a new event :
addEvent - 5.3.2. Delete an event :
deleteEvent - 5.3.3. Select an event :
selectEvent - 5.3.4. Edit an event :
editEvent - 5.3.5. Set the event date :
setDate - 5.3.6. Set the event time :
setTime - 5.3.7. Create a new poll for an event :
addPoll - 5.3.8. Create a new time-based poll for an event :
addTimePoll - 5.3.9. Add options to poll :
addOption - 5.3.10. Get poll result :
displayPoll
- 5.3.1. Create a new event :
- 5.4. Join event commands
- 5.5. [Coming in v2.0] Leave event :
leaveEvent - 5.6. Listing entered commands :
history - 5.7. Exiting the program :
exit - 5.8. Saving the data
- 5.1. View help :
- 6. FAQ
- 7. Command Summary
1. Introduction
EventOrganiser is an application for managing and organising events built for NUS students, also known as EventOrganiser. More importantly, EventOrganiser is optimized for those who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, EventOrganiser can help you to arrange events faster than traditional GUI apps. Interested? Jump to the Section 2, “Quick Start” to get started. Enjoy!
2. Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java version
9or later installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
eventorganiser.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your EventOrganiser.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
listUser: lists all users in EventOrganiser -
addUser` n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com pass/password a/John street, block 123, #01-01` : creates new user namedJohn Doeto EventOrganiser. -
addEvent` n/CS2103 Project Meeting a/SoC Canteen t/Urgent` : adds an event named CS2103 Project Meeting to be held at SoC Canteen. -
exit: exits the app
-
3. How it works, in brief
-
To use the application, you must first create an account using the
addUsercommand, and thenlogin. -
If you are not yet logged in, you can still view event details using
selectEvent, and find events usingfindEventandfindEventByTime, and list events usinglistEvent. -
Without logging in, you can also use the
selectUser,findUser,listUser,listFriends,suggestFriendsByInterestscommands. -
When you are done, simply
logoutorexitthe application.
3.1. Organise an event
-
If you are looking to organise an event, you may do so using the
addEventcommand. -
After creating the event, you may wish to specify the date, time, or specify only after participants have joined.
-
You may create polls to get participants to vote on the details of the event using
addPollandaddPollOption. -
You can create a special TimePoll using
addTimePollafter all participants have joined to decide on a suitable time. This generates poll options based on the NUSMOD schedules of the participants. -
You may decide to
deleteEventafter the event is over, or leave it in the organiser as a form of record.
3.2. Join an event
-
If you are looking to join an event as a participant, you may search for an event to join using the
findEventandfindEventByTimecommands. -
You can also search for other users using the
findUserandlistFriendscommands to see what events they have joined and join that event as well. -
After joining the event using
joinEvent, you can vote in the polls by displaying the poll details usingdisplayPoll. -
You can then add options using
addOption, or simply vote for an option usingvote.
3.3. Manage your account
-
After setting up your account, you can edit your own details using the
editUsercommand, and delete your own account usingdeleteUser. -
You can also search for other users using
suggestFriendsByInterestsand add them as your friend usingaddFriend, or remove them as a friend usingdeleteFriend. -
You can populate your schedule using an NUSMODs link, and also manually add time slots into your schedule.
4. Special Considerations
4.1. XML file
-
We store all of the EventOrganiser data under data/addressbook.xml
-
This file is to be stored securely on the computer. No user is allowed to read or edit the xml file using a text editor.
4.2. User Uniqueness
-
We define the uniqueness of a user by its tuple of NAME and PASSWORD. No two users can have the same NAME and PASSWORD pair. If two users have the same name, then they will have to use different passwords.
-
As user/password pair may allow for a brute-force password attack, we urge all users to choose a secure password that is not easily guessed or commonly used by others.
4.3. Event Uniqueness
-
We define the uniqueness of an event by the event name, location, tags and event organiser. No two events may be identical with respect to these four attributes.
4.4. Timetable
Timetable download guide
To be referenced by any commands that use tt/ prefix.
Format Command tt/ http://modsn.us/XXXX
Example:
* http://modsn.us/eDmp1
* http://modsn.us/H4v8s
Warning: Timetable download will overwrite any existing schedule in the user.
5. Features
Command Format
-
If there than one prefix of the same kind with valid keywords, only the last prefix with valid keywords will be parsed.
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional e.g
n/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
Parameters can be in any order e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
Dates are all specified in
dd-MM-yyyyformat (e.g.01-01-2019, and Times are all specified in 24-hrHH:mmformat (e.g.13:30is 1pm).
5.1. View help : help
Shows all the commands in the application and how to use them.
5.2. User Commands
5.2.1. Add a user : addUser
Adds a new unique user to EventOrganiser.
Format: addUser n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL pass/PASSWORD a/ADDRESS [i/INTEREST]… [tt/TIMETABLE] [t/TAG]…
Examples:
-
addUser n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com pass/password123 a/John street, block 123, #01-01 -
addUser n/Betsy Crowe p/92346611 e/betsycrowe@example.com pass/123 a/Yui Road, block 30, #010-123 i/study t/SOC
5.2.2. Login a user : login
Logs in the user to EventOrganiser. A user must first log in to enable certain commands to be executed.
Format:
login n/USERNAME pass/PASSWORD
Examples:
login n/Alex Yeoh pass/password
5.2.4. List all users : listUser
Shows a list of all users in EventOrganiser.
Format: listUser
5.2.5. Find users by name, phone number, email, address, interest, tag : findUser
Finds users with matching name, phone number, email, address, interest, tag.
Format: findUser [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [i/INTEREST] [t/TAG]
Examples:
|
-
findUser p/87438807 i/dance
Returns any user with the phone number87438807AND interestdance -
findUser n/john e/john@example.com t/teacher
Returns any user with the name87438807AND emailjohn@example.comAND tagteacher
|
-
findUser i/tennis i/soccer
Returns any user with the interestsoccer -
findUser n/Alex n/Bernice n/Li
Returns any user with nameLi
|
-
findUser n/Alex Yu
Returns any user with the nameAlexORYu -
findUser t/SOC FASS SDE
Returns any user with the tagSOCORFASSORSDE
5.2.6. Delete a user : deleteUser
Deletes the currently logged in user from EventOrganiser.
Format: deleteUser
5.2.7. Select a user : selectUser
Selects the user identified by the index number used in the displayed user list.
Format: selectUser INDEX
Examples:
-
listUser
selectUser 2
Selects the 2nd user in EventOrganiser. -
findUser Betsy
selectUser 1
Selects the 1st user in the results of thefindcommand.
5.2.8. Edit a user : editUser
Edits the currently logged-in user in EventOrganiser.
Format: editUser [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [pass/PASSWORD] [i/INTEREST]… [tt/TIMETABLE] [su/SCHEDULE_UPDATE] [t/tags]…
Examples:
-
login n/Alex Yeoh pass/password
editUser p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com
Edits the phone number and email address of the userAlex Yeohto be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
login n/Alex Yeoh pass/password
editUser n/Betsy Crower t/
Edits the name of the userAlex Yeoh`to be `Betsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
5.2.9. Add a friend : addFriend
Adds a person to the logged-in user’s friend list.
Format: addFriend INDEX
Examples:
-
addFriend 2
User specified atINDEX2 is added to the logged-in user’s friend list.
5.2.10. Delete a friend : deleteFriend
Deletes a person from the logged-in user’s friend list.
Format: deleteFriend INDEX
Examples:
-
deleteFriend 2
User specified atINDEX2 is deleted from the logged-in user’s friend list.
5.2.11. Suggest friends based on similar interests : suggestFriendsByInterests
Suggest friends for an existing user in EventOrganiser that have at least one similar interest with the selected user.
Format: suggestFriendsByInterests INDEX
Examples:
-
suggestFriendsByInterests 1
Displays users in EventOrganiser that have at least one similar interest with the selected 1st user, and are not yet in the selected user’s friend list.
5.2.12. List all friends of a user : listFriends
List all the users that are in the friend list of the selected user.
Format: listFriends INDEX
Examples:
-
listFriends 1
List all the users who are in the friend list of the 1st user in EventOrganiser.
5.2.13. Get free time between users : maxSchedule
Compares the schedule of multiple users and return a string of common free time slots. LIMIT is a XXXX-XXX specified timing to limit the time range displayed.
Format: maxSchedule INDEX INDEX… [sl/ LIMIT]…
Example:
-
maxSchedule 1 2
Compares the schedule of users of index 1 and 2 and return a string of all common free time. -
maxSchedule 1 2 sl/ 0800-0900
Compares the schedule of users of index 1 and 2 and return a string of common free time limited to 0800 to 0900 hours inclusive.
5.3. Create and confirm event commands
5.3.1. Create a new event : addEvent
Adds a new event to EventOrganiser.
Format: addEvent n/NAME a/LOCATION [t/TAG] …
Examples:
-
addEvent n/NUS Tennis Welcome Session a/SOC Canteen t/Public -
addEvent n/CS1101S Meet-up a/UTown t/ByInvite
5.3.2. Delete an event : deleteEvent
Deletes the specified event from EventOrganiser.
Format: deleteEvent INDEX
Examples:
-
listEvent
deleteEvent 2
Deletes the 2nd event in EventOrganiser.
5.3.4. Edit an event : editEvent
Edits an existing event in EventOrganiser. Only the event name, location and tags may be edited using this command.
Format: editEvent [n/NAME] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG] …
|
At least one of the optional fields must be provided. |
Examples:
-
editEvent n/CS2102 Discussion t/URGENT
Edits name of the currently selected event toCS2102 Discussionand its tag toURGENT.
5.3.5. Set the event date : setDate
Sets the event date.
Format: setDate d/DAY-MONTH-YEAR
Examples:
-
setDate d/08-09-2018 -
setDate d/11-12-2019
5.3.6. Set the event time : setTime
Sets the event time.
Format: setTime t1/HOUR:MINUTE t2/HOUR:MINUTE
Examples:
-
setTime t1/23:00 t2/23:30 -
setTime t1/13:30 t2/14:00
5.3.7. Create a new poll for an event : addPoll
Sets up a new poll for the pre-selected event with the specified name.
Format: addPoll n/POLL_NAME
-
addPoll n/Date
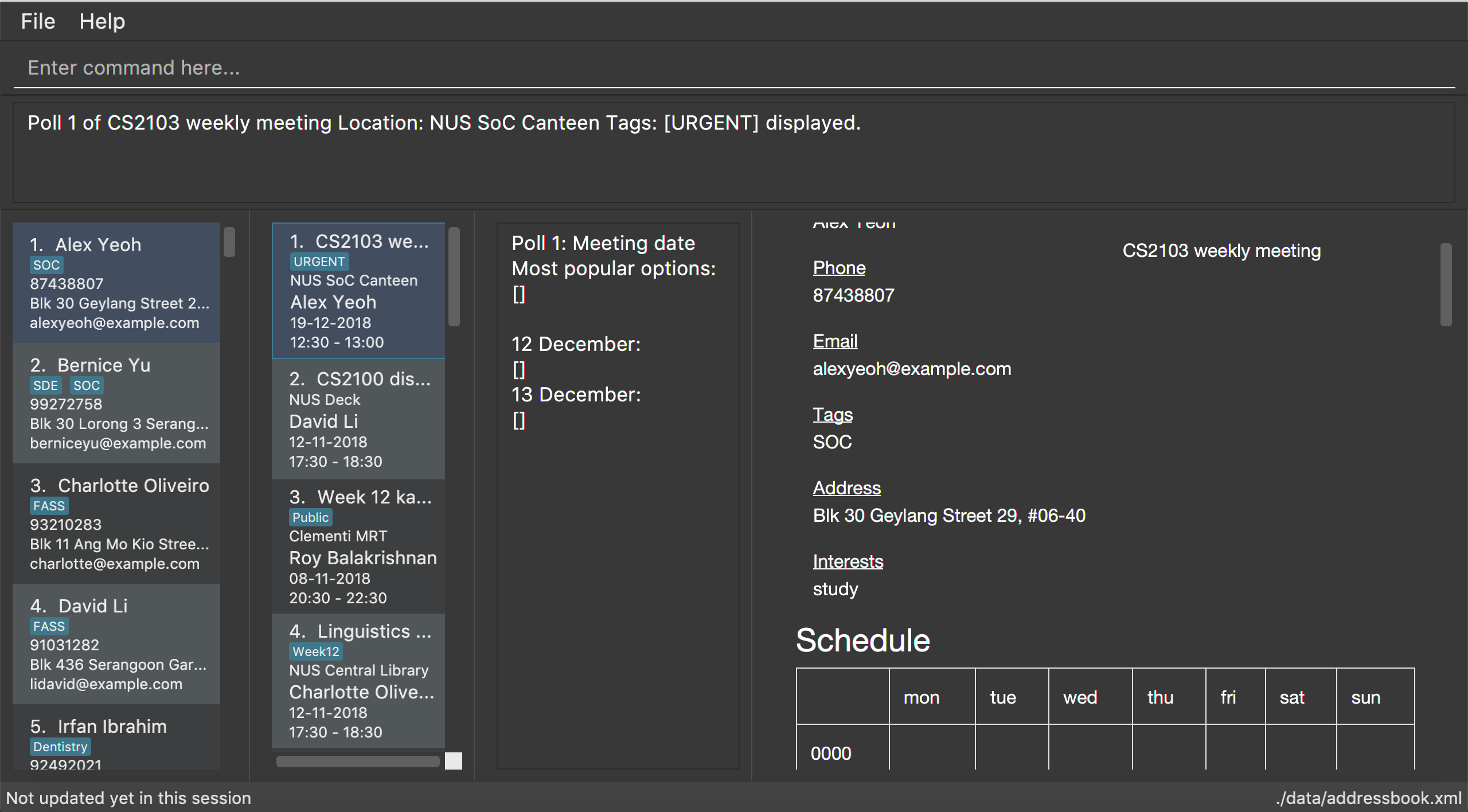
Upon adding a new poll, only the index and name of the poll is displayed, as shown. The event organiser can then proceed to add options to the poll. Selecting the event again using theselectEventcommand displays the list of all polls in the event.
The following screenshot shows the outcome of this command.
5.3.8. Create a new time-based poll for an event : addTimePoll
Sets up a new time-based poll for the event with the specified name after all users have joined.
Format: addTimePoll d1/DAY-MONTH-YEAR d2/DAY-MONTH-YEAR
Examples:
-
addTimePoll d1/08-09-2018 d2/10-09-2018
5.3.9. Add options to poll : addOption
Add new poll option in the specified poll.
Format: addOption i/POLL_INDEX o/POLL_OPTION
Examples:
-
addOption i/1 o/Play chess
Adds an option to the first poll of the selected event, where the option isPlay chess. This option would be relevant in the context of a poll for an appropriate activity. -
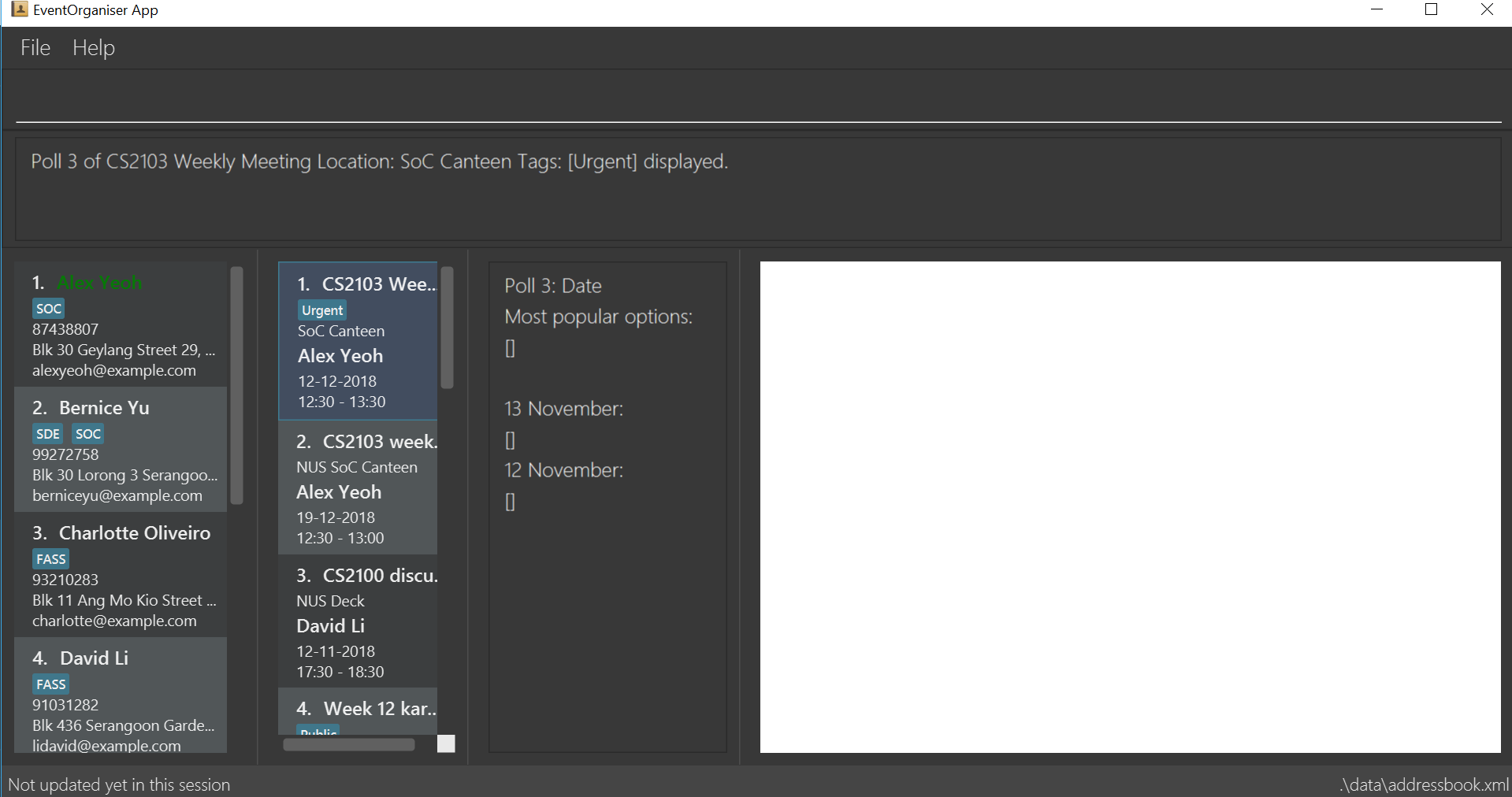
addOption i/3 o/12 November
addOption i/3 o/13 November
In the following example, the options12 Novemberand13 Novemberhave been added to the poll. Since there are no voters yet, the most popular options list is empty.
5.3.10. Get poll result : displayPoll
Gets the result of a specified poll.
Format: displayPoll i/POLL_INDEX
Examples:
-
displayPoll i/1
Displays the poll with index 1 associated with the already selected event, if it exists in the event.
5.4. Join event commands
5.4.1. Find event by the name of the event : findEvent
Finds events based on the attributes of the event: event name, event location, date, start time, event organiser, and event participants.
Format: findEvent [e/EVENT_NAME] [a/LOCATION] [d/DATE] [t1/START_TIME] [on/ORGANISER_NAME] [pn/PARTICIPANT_NAME]
Examples:
-
findEvent e/CS2103 weekly meeting on/Alex Yeoh
Finds all events with the name "CS2103 weekly meeting" and with the organiser whose name is "Alex Yeoh".
5.4.2. Find event by a time interval: findEventByTime
Finds events held on a specific date, and is held between a start and end time.
Format: findEvent d/DAY-MONTH-YEAR t1/HOUR:MINUTE t2/HOUR:MINUTE
Examples:
-
findEvent d/12-12-2018 t1/12:00 t2/18:00
Finds all events held between 12pm and 6pm on 12 December 2018.
5.4.3. List all events : listEvent
Shows a list of all events in EventOrganiser.
Format: listEvent
5.4.4. Join event : joinEvent
Joins event identified by event index in the event list.
Format: joinEvent INDEX
Examples:
-
joinEvent 2
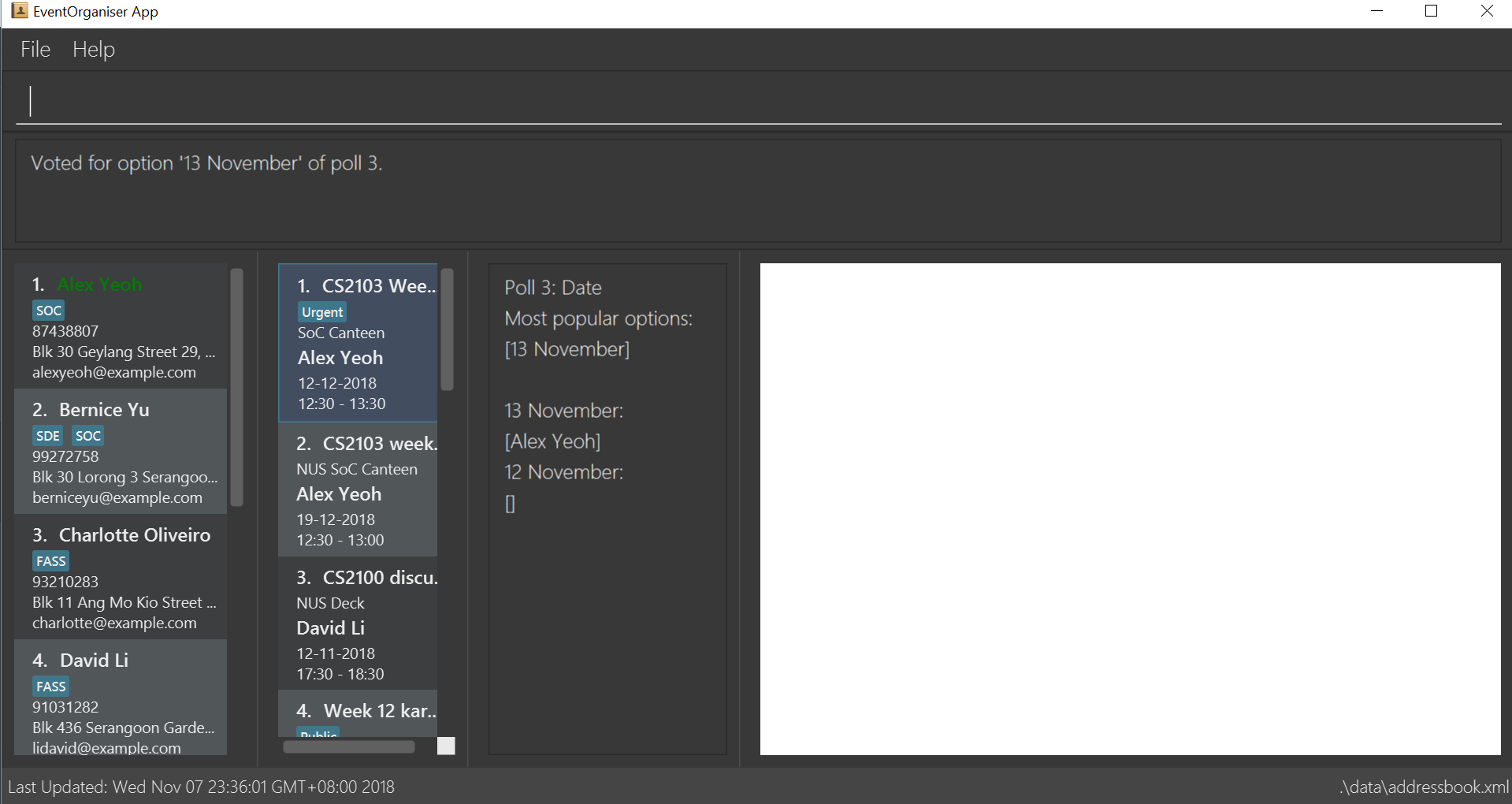
5.4.5. Vote for date : voteOption
Vote for a option specified in a specified poll, if there is one.
Format: voteDate i/POLL_INDEX o/POLL_OPTION
Examples:
-
voteDate i/3 o/12 August -
voteDate i/3 o/13 November
In the following example,Alex Yeohhas voted for13 November. Since it is the most popular option,13 Novemberappears in the most popular options list.
5.5. [Coming in v2.0] Leave event : leaveEvent
Leaves event identified by event index in the event list.
Format: leaveEvent INDEX
Examples:
-
leaveEvent 2
5.6. Listing entered commands : history
Lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
Format: history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
5.7. Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
5.8. Saving the data
EventOrganiser data is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
6. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous EventOrganiser folder.
7. Command Summary
7.1. User commands
-
Help :
help -
Add User
addUser n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL pass/PASSWORD a/ADDRESS [t/TAG] [i/INTEREST]…
e.g.addUser n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com pass/password a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague
-
Login
login n/NAME pass/PASSWORDe.g.login n/Alex Yeoh pass/password -
Logout
logout -
List User :
listUser -
Find User (by name, phone number, email, address, interest, or tag) :
findUser [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG] [i/INTEREST]
e.g.findUser n/Alex Yeoh -
Delete User :
deleteUser
e.g.deleteUser
-
Add a friend
addFriend INDEXe.g.addFriend 2 -
Delete a friend
deleteFriend INDEXe.g.deleteFriend 2 -
Suggest friends based on similar interests :
suggestFriendsByInterests INDEXe.g.suggestFriendsByInterests 1 -
List all friends :
listFriends INDEXe.g.listFriends 1
-
Edit User :
editUser [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [i/INTEREST]… [t/TAG]… [tt/TIMETABLE] [su/SCHEDULE_UPDATE]
e.g.editUser n/Alex Yeoh e/jameslee@example.com
e.g.editUser tt/ http://modsn.us/H4v8s
e.g.editUser su/ monday 0000 -
Select User :
selectUser INDEX
e.g.selectUser 2 -
History :
history
-
Free time between persons:
maxSchedule INDEX INDEX … [sl/ LIMIT]
e.g.maxSchedule 1 2
e.g.maxSchedule 1 2 3 sl/ 0800-0900
7.2. Event organiser commands
-
Add Event :
addEvent n/EVENT_NAME a/LOCATION [t/TAG]…
e.g.addEvent n/CS2103 Project Meeting a/SoC Canteen t/Urgent -
Delete Event :
deleteEvent INDEX
e.g.deleteEvent 1 -
Edit Event :
editEvent [n/NAME] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG] …
e.g.editEvent n/CS2102 Meeting t/URGENT t/ByInvite -
Select Event :
selectEvent INDEX
e.g.selectEvent 1 -
Add Poll :
addPoll n/POLL_NAME
e.g.addPoll n/Activity -
Add Option :
addOption i/POLL_INDEX o/POLL_OPTION
e.g.addOption i/1 o/Play games -
Add Time Poll :
addTimePoll d1/DAY-MONTH-YEAR d2/DAY-MONTH-YEAR
e.g.addTimePoll d1/01-12-2018 d2/02-12-2018 -
Display Poll :
displayPoll INDEX
e.g.displayPoll 1 -
Set Event Date :
setDate d/DAY-MONTH-YEAR
e.g.setDate d/12-12-2018 -
Set Event Time :
setTime t1/HOUR:MINUTE t2/HOUR:MINUTE
e.g.setTime t1/12:30 t2/13:45
7.3. Event participant commands
-
Join Event :
joinEvent INDEX
e.g.joinEvent 1 -
Vote :
vote i/POLL_INDEX o/POLL_OPTION
e.g.vote i/1 o/Play games -
Find Event With Attributes :
findEvent [e/EVENT_NAME] [a/LOCATION] [d/DAY-MONTH-YEAR] [t1/HOUR:MINUTE (START_TIME)] [on/ORGANISER_NAME] [pn/PARTICIPANT_NAME]
e.g.findEvent d/19-12-2018 on/Alex Yeoh
e.g.findEvent a/NUS SoC Canteen -
Find Event by Time :
findEventByTime d/DAY-MONTH-YEAR t1/HOUR:MINUTE t2/HOUR:MINUTE
e.g.findEventByTime d/19-12-2018 t1/12:30 t2/13:45 -
List Events :
listEvent
e.g.listEvent